What is Blockchain?
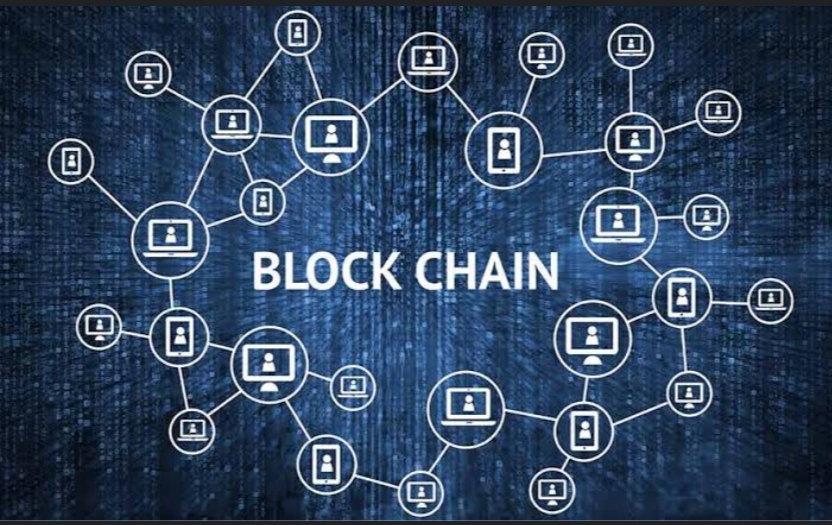
Blockchain is like a digital diary that is shared among a group of people and everyone in the group can make an entry in this digital diary but once the entry is made it cannot be changed, it’s there forever and everyone can see it. This diary is decentralised and it is stored in many computers across the world. Basically it’s a method of recording information that makes it impossible for the system to be changed, hacked or manipulated.
How Blockchain works:

The information that needs to be recorded could be anything of value like money, property, contacts or even votes in elections. So it is a transparent, simple , decentralised diary that records transactions across many computers.
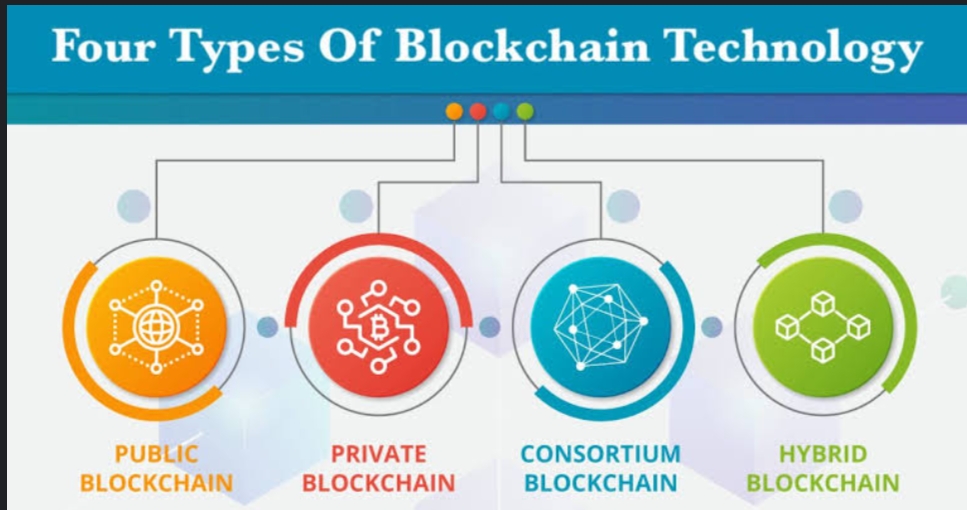
Various types of Blockchains:-
There are four main types of blockchain networks: public blockchains, private blockchains, consortium blockchains and hybrid blockchains.
1. Public Blockchains:- This is the first type of Blockchain technology. Public Blockchains removes the problems that come with centralisation including less security and transparency. Public Blockchains is where cryptocurrency like Bitcoin originated and helped to popularize distributor ledger technology (DLT). DLT doesn’t store information in any one place, instead distributing it across a peer to peer network. One of the advantages of public blockchains is that they are completely independent of organizations, so if the organization that started it ceases to exist the public blockchain will still be able to run, as long as there are computers still connected to it.
2. Private Blockchains:- A blockchain network that works in a restrictive environment like a closed network, or that is under the control of a single entity, is a private blockchain. They are also known as permissioned Blockchain or enterprise Blockchain. A private blockchain network can determine which nodes can view, add or change data. It can also prevent third parties from accessing certain information.
3. Hybrid Blockchain:- Hybrid Blockchain is a type of Blockchain that combines the elements of both public and private Blockchains. One of the big advantages of hybrid blockchain is that, because it works within a closed ecosystem, outside hackers can’t mount a 51% attack on the network.
4. Consortium Blockchain:- Consortium blockchain is a private blockchain with limited access to a particular group, eliminating the risks that come with just one entity controlling the network on a private blockchain. Consortium blockchain tends to be more secure, scalable and efficient than a public blockchain network.

Application of Blockchain technology:-
Blockchain technology can be utilized in multiple industries including Financial Services, Healthcare, Government, Travel and Hospitality, Retail and CPG. Some other areas are also where the Blockchain is emerging, like Monitoring the supply chains, audit trails, Medicine monitoring, Data sharing, Copyright and Royalty, Tax Regulation, and Equity trading. If we will talk from a career point of view: Blockchain is a rising field. In the market right now, Blockchain developers are significantly fewer, and the demand for developers will be very high in the upcoming need.
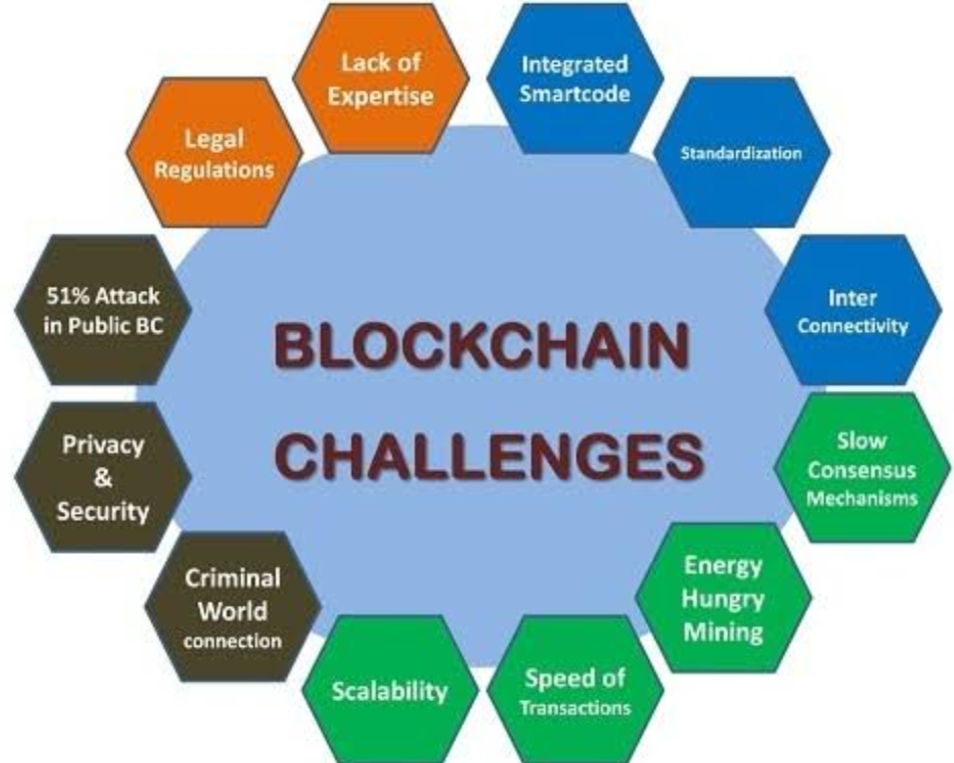
Challenges and limitations of Blockchains:-
While blockchain technology holds immense potential, it is not without its challenges and limitations that need to be addressed for widespread adoption.
• Scalability and transaction speed:-
One of the primary challenges facing blockchain is scalability, as the size of the blockchain network and the number of transactions increase. Striking a balance between scalability and decentralization remains a significant hurdle for blockchain developers.
• Energy consumption and environmental impact:–
Blockchain networks, particularly those based on PoW consensus mechanisms, require significant computational power, leading to high energy consumption. Developing energy-efficient solutions and transitioning to more sustainable consensus algorithms is a crucial concern for the blockchain community.
• Legal and regulatory hurdles:-
As blockchain continues to disrupt traditional industries, legal and regulatory frameworks struggle to keep pace. Uncertainty surrounding issues like data privacy, intellectual property rights, and cross-border regulations pose challenges to the widespread implementation of blockchain technology.
• Data privacy and confidentiality concerns:-
While blockchain provides strong security measures, the inherent transparency raises concerns about the privacy and confidentiality of sensitive data. Striking the right balance between transparency and privacy is crucial for blockchain to gain widespread acceptance
Summary: The Revolutionary Nature of Blockchain Technology:-
In summary, blockchain technology has emerged as a groundbreaking force, transforming industries and reshaping our digital landscape. With its decentralized, transparent, and secure nature, blockchain promises to revolutionize various sectors, empower individuals, and pave the way for a future driven by trust, efficiency, and innovation.




